Capstone Project – A Complete Guide A capstone project is sometimes the...
Read MoreDissertation Abstract - A Complete Guide
A dissertation abstract may be a compact outline of a dissertation’s content, usually settled at the document’s start. Despite its brevity, it holds vital importance because it provides the primary impression of your analysis, summarizing the matter, methods, results, and conclusions in a condensed format. The dissertation abstract aims to give readers a transparent summary of the complete work, permitting them to determine whether or not to browse the total treatise or explore its findings more.
For many, the abstract is usually the primary section of their dissertation to be written. Nevertheless, its importance cannot be immoderate. A literary dissertation abstract can give a comprehensive shot of the dissertation’s content while being concise and to the purpose. During this diary, we’ll explore a treatise abstract, the way to write one, a sample abstract, and tips to make your abstract stand out.
In this blog brings you:
What exactly is a Dissertation Abstract?
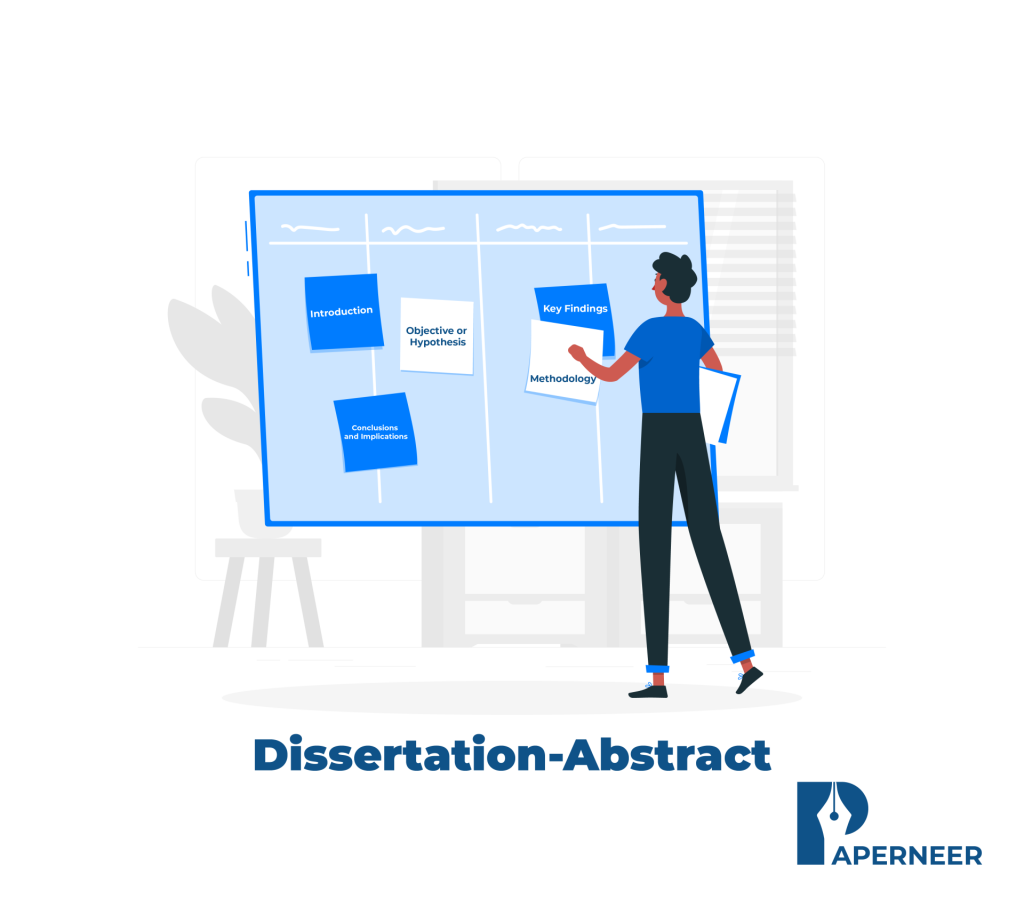
A dissertation abstract is a summary of your entire thesis. It usually spans around 200-300 words and condenses all significant aspects of your analysis and the matter statement, analysis objectives, methodology, findings, and conclusions. Typically thought of as an essential part of the document, it’s the primary section that several readers encounter, and it will influence their call to interact with the remainder of the work.
The abstract lets readers quickly verify whether the thesis aligns with their analysis interests or is relevant to their field of study. In addition, it ought to be written in a way that gives a transparent understanding of the dissertation’s purpose and outcomes, even while not delving into the document’s main points. For this reason, crafting an efficient abstract requires a deep understanding of your analysis and the ability to condense advanced data into a concise format.
How to Write a Dissertation Abstract
Writing an impactful dissertation abstract is often tricky. However, it’s achievable with the proper approach. Below are the essential steps to follow:
Begin with the analysis drawback or Question
Start your abstract by outlining the drawbacks or analysis questions your dissertation addresses the most. This is often the inspiration for your work and will capture the reader’s attention. The analysis drawback or Question should be briefly expressed but clearly outlined, providing a terse summary of the problem your analysis seeks to resolve.
Summarize the analysis Objectives
After characteristic the analysis drawback, progress to outlining the objectives of your study. What did your analysis aim to achieve? Here, you ought to briefly describe the scope of your analysis, the precise goals you came into being to accomplish, and the hypothesis you wanted to check.
Describe Your Methodology
Next, give a summary of the methodology employed in your analysis. This section should be terse and justify the analysis style, information assortment strategies, and any tools or techniques you want to analyze the info. The methodology section ought to supply only enough detail to assist the reader in perceiving how you approached your analysis while not being slowed down in specifics.
Highlight the Key Findings
The most vital part of the thesis abstract is the presentation of your findings. This could be a summary outline of the key results of your study. What did your analysis reveal? Avoid presenting too technical information; instead, target the key insights that emerged from your work.
Conclude along with your analysis. Implications
Lastly, conclude your abstract by summarizing the impact of your findings. What contributions will your analysis build to the present body of knowledge? Discuss the potential impact of your results on the sector and any recommendations for future research or observation. This final section ought to provide closure and significance for your work.
Dissertation Abstract Sample
To help you better perceive a way to structure your dissertation abstract, here may be a sample:
Sample Dissertation Abstract:
“This study explores the link between social media usage and academic performance among faculty students. The analysis aims to see whether or not time spent on social media platforms correlates with lower grades and diminished tutorial performance. A survey was conducted with two hundred students, gathering information on their social media habits and tutorial achievements. The results show a major negative correlation between time spent on social media and GPA. These findings suggest that students who spend over ten hours per week on social media have a lower GPA than those who spend less time on these platforms. The study concludes by recommending universities introduce workshops on time management and the accountable use of social media to assist students in improving their tutorial performance. Future research is required to look at the long-run effects of social media on academic success.”
Tips for Writing an Effective Dissertation Abstract
When writing your dissertation abstract, keep the following tips in mind to make sure it’s effective and impactful:
Keep It Concise
The abstract should be a quick outline, usually 200-300 words. Be pithy and avoid unessential details. Specialize in presenting the foremost vital aspects of your analysis while not overwhelming the reader.
Use Clear and easy Language
While your thesis may use complicated words and advanced ideas, the abstract should be clear and straightforward. Avoid jargon or, to a fault, technical terms that might confuse a reader unfamiliar with your specific field.
Use active and robust Verbs
Though the abstract may sometimes need passive for formality, specialize in active once attainable. Active conveys clarity and makes the text a lot of partaking. For example, “The study found” is much more direct than “The study found it.”
Avoid Citations
The abstract mustn’t embody citations from different works. It’s a self-contained outline of your thesis. There’s no need to reference different studies or theories in this section because the focus should be entirely on your work.
Revise and Edit
After drafting your abstract, it’s vital to revise and refine it. Make sure that it aligns with the general content of your thesis and accurately represents the analysis and findings. Writing for clarity, terseness, and flow can facilitate and guarantee your abstract effectively communicates the key points.
Conclusion
A dissertation abstract is over simply a summary—it’s a strong tool to grab the eye of your audience and lure them to browse your entire thesis. By following the rules made public higher, you’ll be able to craft an abstract that effectively communicates the essence of your analysis in an elliptical, however impactful manner. Remember, your abstract is the gateway to your dissertation. Thus, it must be clear, informative, and engaging.
Whether you are troubled with condensing your work or just searching for tips to improve your abstract, that specialize in clarity, structure, and relevance can ensure that your dissertation abstract stands out as a powerful introduction to your analysis.
Say goodbye to Mistakes in Term Papers
Avoid Errors in Term Papers Writing a theme may be a vital tutorial task that needs careful designing and...
Read MoreUnraveling the Stories: Autobiography vs Biography
Autobiography vs Biography Understanding the excellence between autobiography and biography is crucial for...
Read More